Article Overview:
Classification of SMT Conveyors Based on Transmission Method
1. Chain Conveyor
2. Belt Conveyor
3. Roller Conveyor
4. Bull`s Eye Conveyor
Classification PCB Assembly Conveyor Based on Function
1. Standard SMT Conveyor
2. Multi-Function SMT PCB Conveyors
2-1. SMT Link/Inspection Conveyor
2-2. SMT PCB Cooling Conveyor
2-3. SMT PCB Reject Conveyor
2-4. SMT PCB Telescopic Conveyor
2-5. SMT PCB Flipper / Inverter
2-6. SMT PCB Turn Conveyor / Diverter
2-7. SMT PCB Translation Shuttle Conveyor
2-8. SMT PCB Change Edge Machine ( PCB Rotating Conveyor )
3. Automated Conveyor (Inline SMT Conveyor)
Classification SMT Line conveyor Based on Application
1. SMT production line
2. Wave soldering production line
3. Plug-in component assembly production line
4. Inspection and testing production line
Classification PCB Conveyor Based on Material
1. Metal Conveyors
2. Plastic Conveyors
Classification PCB Handling Conveyor Based on Configuration
1. PLC-Based Conveyor
2. Microcontroller-Based Conveyor
Classification SMT Conveyor Belt Based on Speed
1. Low-Speed PCB Conveyor
2. High-Speed PCB Conveyor
How to choose the right SMT conveyor for your production?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) plays a crucial role in modern PCB assembly, and SMT conveyors are essential for transporting PCB boards efficiently through various production stages. Different types of SMT PCB conveyors are designed to meet different needs in SMT production lines.
Whether you`re a PCB manufacturer, equipment integrator, SMT machine suppliers or SMT process engineer, understanding the different types of conveyors can help you select the right PCB handling solution for your needs.
This article will explore the various types of PCB handling conveyors, their working principles, main features, and application scenarios.

Classification of SMT Conveyors Based on Transmission Method
1. Chain Conveyor (PCB Conveyor Chain)
A chain conveyor uses a chain-driven mechanism to transport PCB boards, making it suitable for high-speed, large-volume production lines.
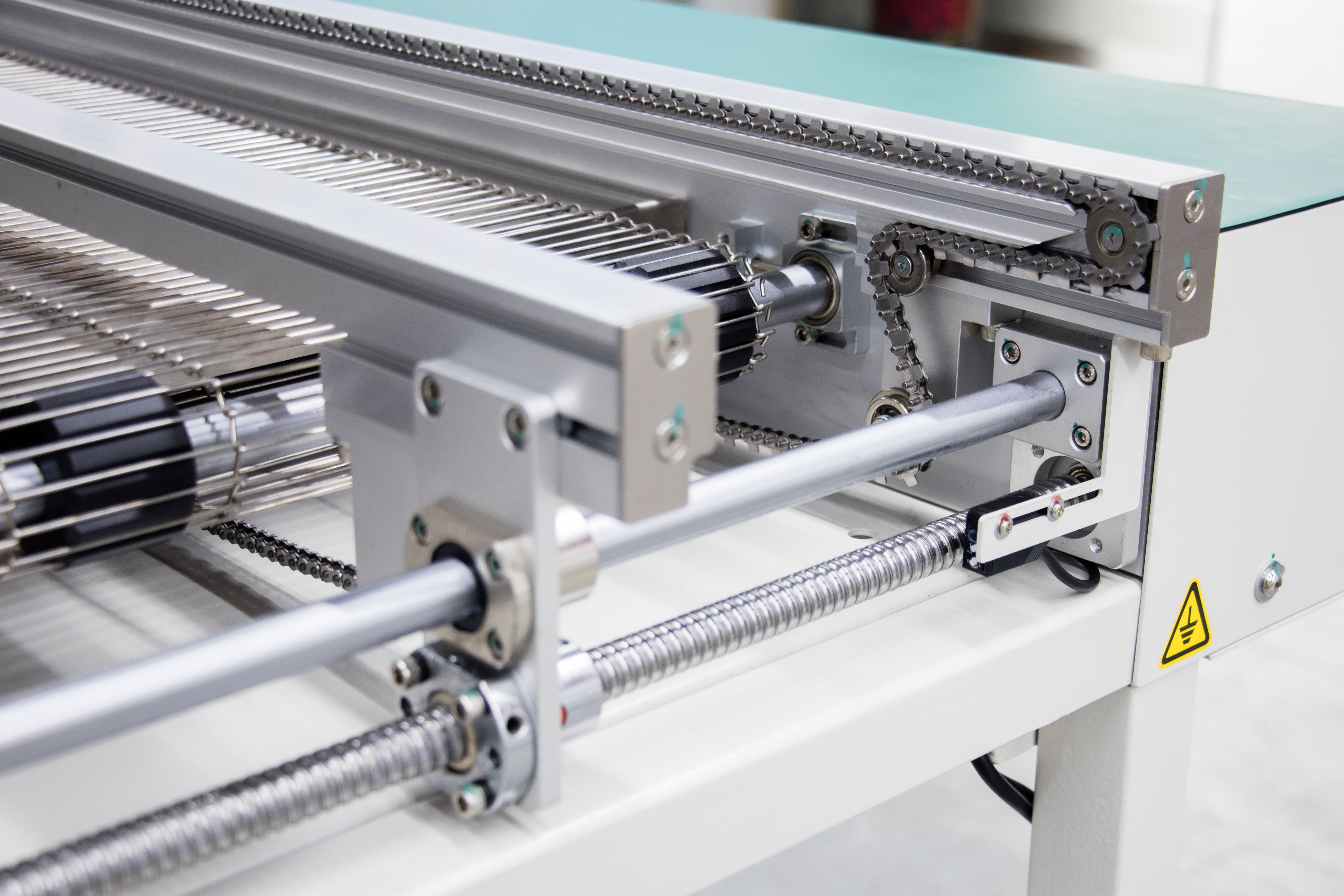

Working Principle:
The chain conveyor uses metal chains or anti-static plastic chains as the transmission medium, and drives the chains through motors to ensure smooth transmission of PCBs in the production line.
Main Features:
-
High temperature resistance: suitable for PCB transmission after high temperature processes such as reflow soldering and wave soldering.
-
Strong bearing capacity: suitable for heavier or larger PCB boards, such as server motherboards, power modules, etc.
-
Anti-static design: ESD protection chain can be optionally equipped to reduce the impact of static electricity on PCB.
PCB transfer in SMT production lines, especially after high temperature or heavy PCB transfer.
PCB transfer before and after reflow soldering and wave soldering.
Large size or special material PCB (such as metal substrate) transfer requirements.
2. Belt Conveyor (PCB Conveyor Belt)
This type of workstation uses a belt conveyor to transport PCB boards, typically positioned horizontally or at an incline, and is suitable for medium-to-large scale production.

Working Principle:
The belt-type PCB conveyor uses rubber belts or anti-static PU belts as the transmission medium, and relies on rollers or drive wheels to drive the belts to achieve PCB transmission.
Main Features:
Smooth transmission: Reduce PCB vibration, suitable for processes with high stability requirements.
Lightweight and flexible: Simple structure, suitable for various production line layouts.
Wide range of applications: Can be used for various PCB sizes and thicknesses without restrictions.
Application:
PCB conveying before and after SMT patching.
Suitable for the transmission of standard PCB or small electronic components.
Requires low noise and low vibration production environment, such as high-precision electronic manufacturing.
3. Roller Conveyor (PCB Transfer Conveyor)
A roller conveyor workstation uses multiple parallel rollers to transfer PCB boards, commonly used for short-distance transport, and is suitable for small-to-medium-scale production lines.

Working Principle:
The rollers are driven by operators or machines, transferring PCBs via the physical rolling action. This system is well-suited for irregularly shaped or heavier PCBs.
Main Features:
Cost-effective, easy to maintain, and supports heavier loads, making it ideal for electronic components and irregularly shaped or heavier PCBs.
Adjustable to different PCB board sizes, ensuring versatility for various applications.
Supports both manual and automated PCB transfer for flexible operations.
Simple maintenance and lower operational costs, offering long-term efficiency.
Application:
SMT buffer conveyors between different processing stages.
PCB inspection conveyor setups for manual inspection.
Small or medium-sized production lines, capable of handling various PCB sizes.
Transporting heavier PCBs or those requiring special handling.
4. Bull`s Eye Conveyor
The bull's eye docking station adjusts the PCB to a specific direction through a rotating platform to ensure accurate docking with downstream equipment. It is often used in SMT production lines to enter the plug-in process after patching.

Features:
Precise rotation: The PCB rotation angle can be controlled to ensure accurate docking.
High adaptability: It can adapt to production process requirements in different directions and optimize the layout of the production line.
Strong stability: It adopts a high-precision rotating mechanism to ensure smooth operation and reduce PCB movement errors.
What type of PCB Handling Conveyor do you prefer?>>>
Classification PCB Assembly Conveyor Based on Function
1. Standard SMT Conveyor (Conveyor for PCB)
Used to transfer PCB boards in SMT production lines and connect standard conveying devices between different devices.
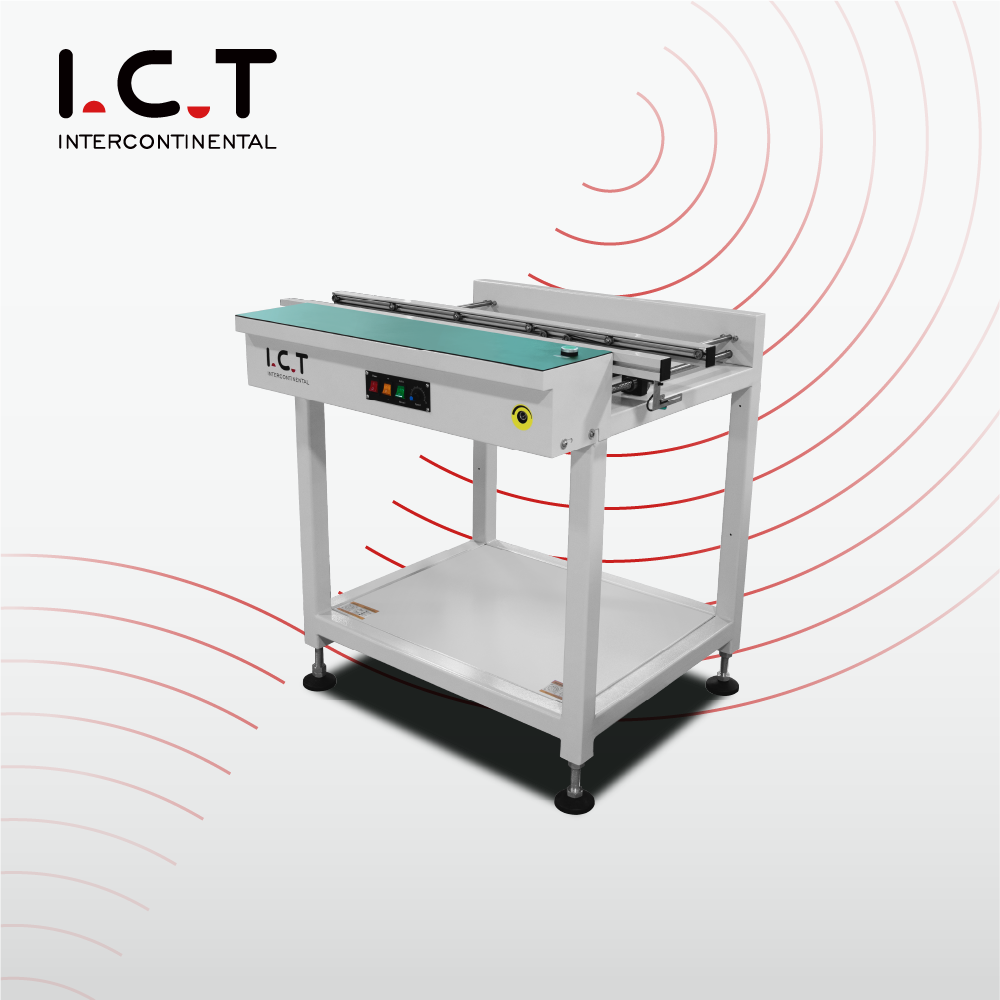

Working principle:
The motor is driven by a belt or chain to transfer the PCB along the track to the next process.
Features:
simple structure, low cost, suitable for all SMT production lines.
Get a Quote >>
2. Multi-Function SMT PCB Conveyors
A multifunctional conveyor is a device that integrates multiple functions in one, aiming to improve the flexibility and efficiency of the production line.
Compared with traditional single-function SMT conveyor, multifunctional conveyor usually have the following types:
2-1. SMT Link/Inspection Conveyor
Application:
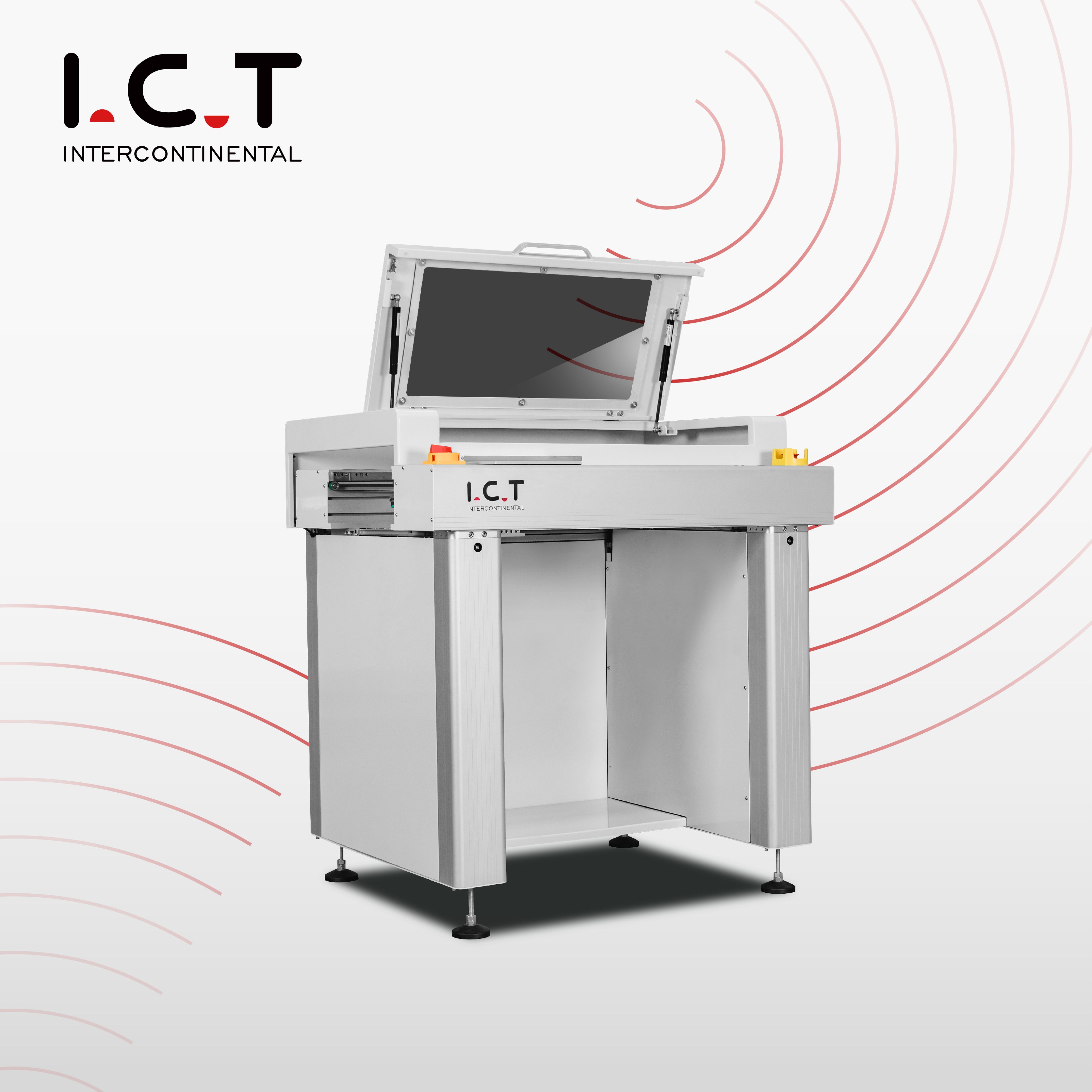

Working principle:
Provides a stable PCB transfer platform, equipped with lighting and magnifying glass for manual visual inspection or rework.
Features:
PCB can be stopped individually, the operator can inspect or rework, some models support dual tracks or adjustable speed.
Get a Quote >>
2-2. SMT PCB Cooling Conveyor
Application:
After reflow soldering/wave soldering/selective soldering, ensure the PCB is at a safe temperature before entering the inspection or assembly process.
Before temperature-sensitive processes, such as coating or specific assembly steps.
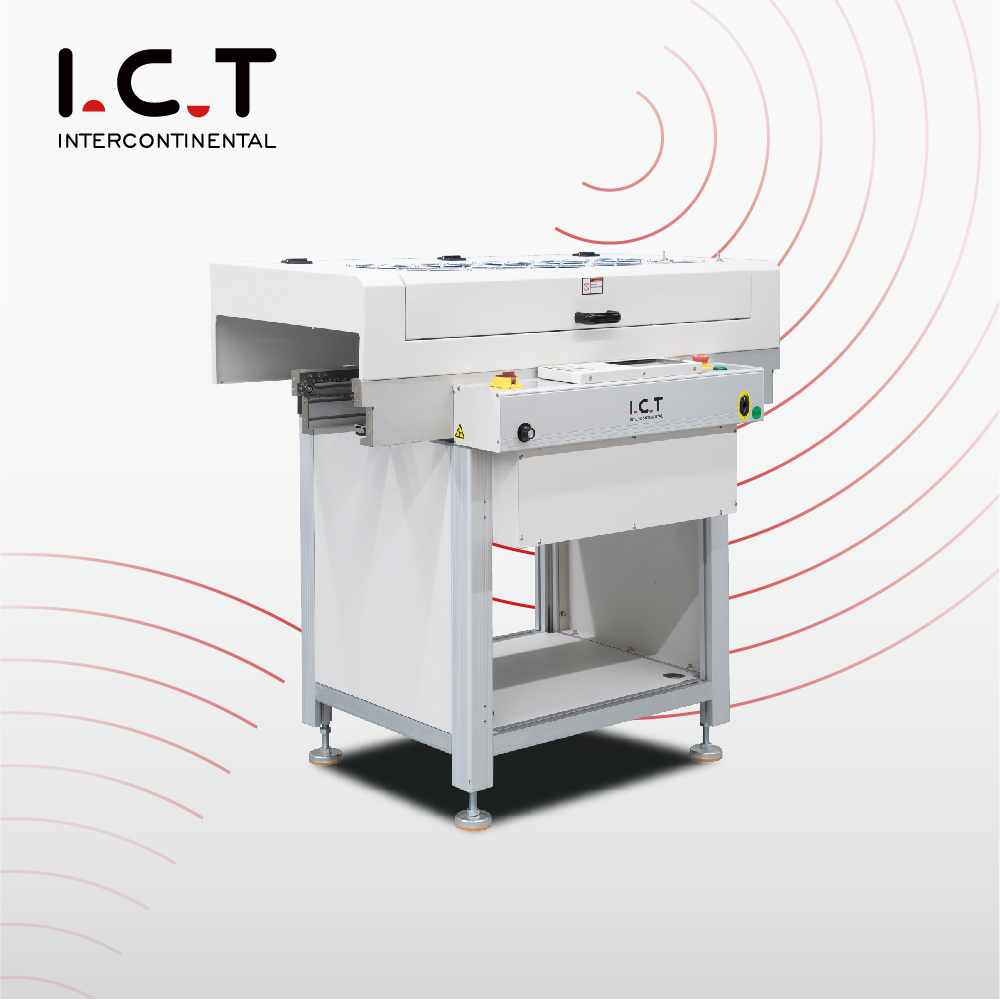

Working Principle:
The PCB cooling conveyor uses natural or air cooling to lower PCB temperature, ensuring stable transfer to inspection or assembly.
Features:
The PCB cooling conveyor quickly cools using natural or air cooling, supports adjustable airflow, ensures stable operation, and is widely used for temperature management after soldering.
Get a Quote >>
2-3. SMT PCB Reject Conveyor
Application:
Screening of defective products on the production line;
Used in conjunction with AOI, SPI, ICT and other inspection equipment;
Preventing defective products from entering the next process and improving the yield rate.
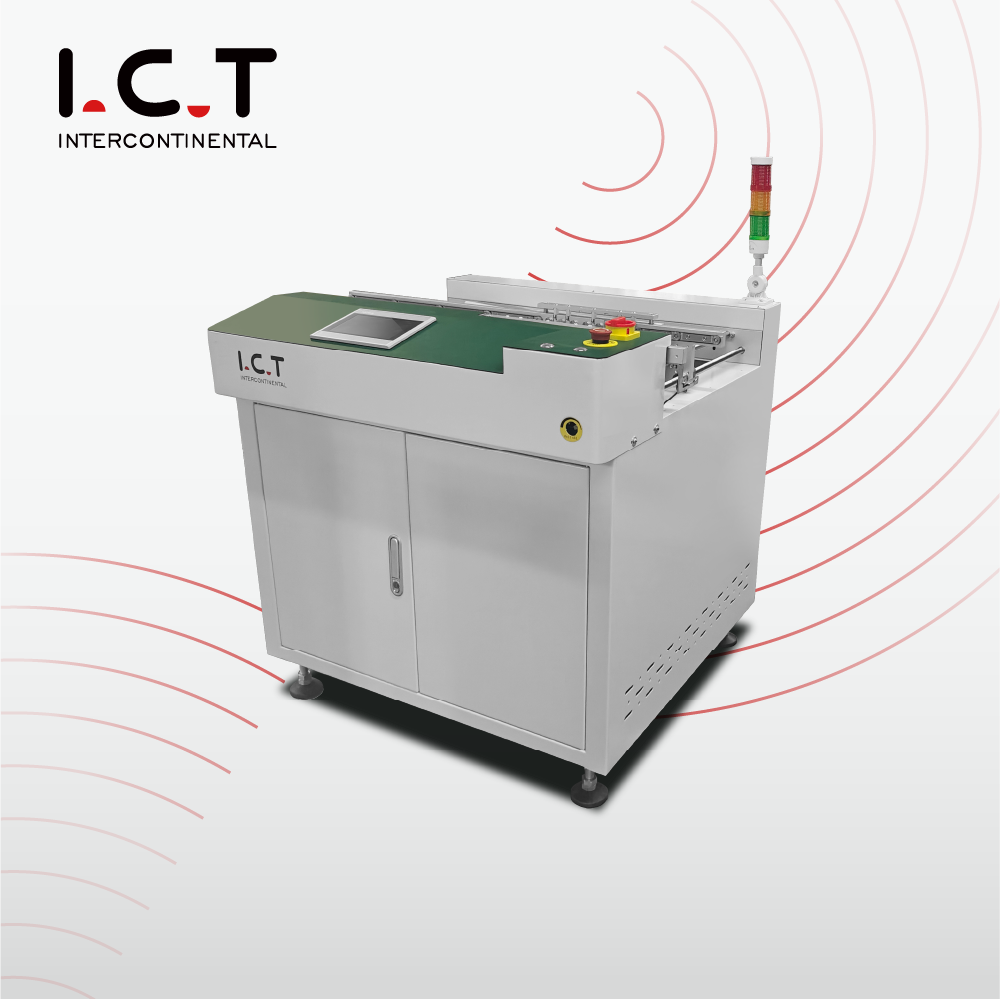

Working principle:
Detect PCB status and automatically divert PCBs that do not meet the standards to a dedicated rework area.
Features:
High detection accuracy, manual or automatic screening, and improved production quality management.
Get a Quote >>
2-4. SMT PCB Telescopic Conveyor
Application:
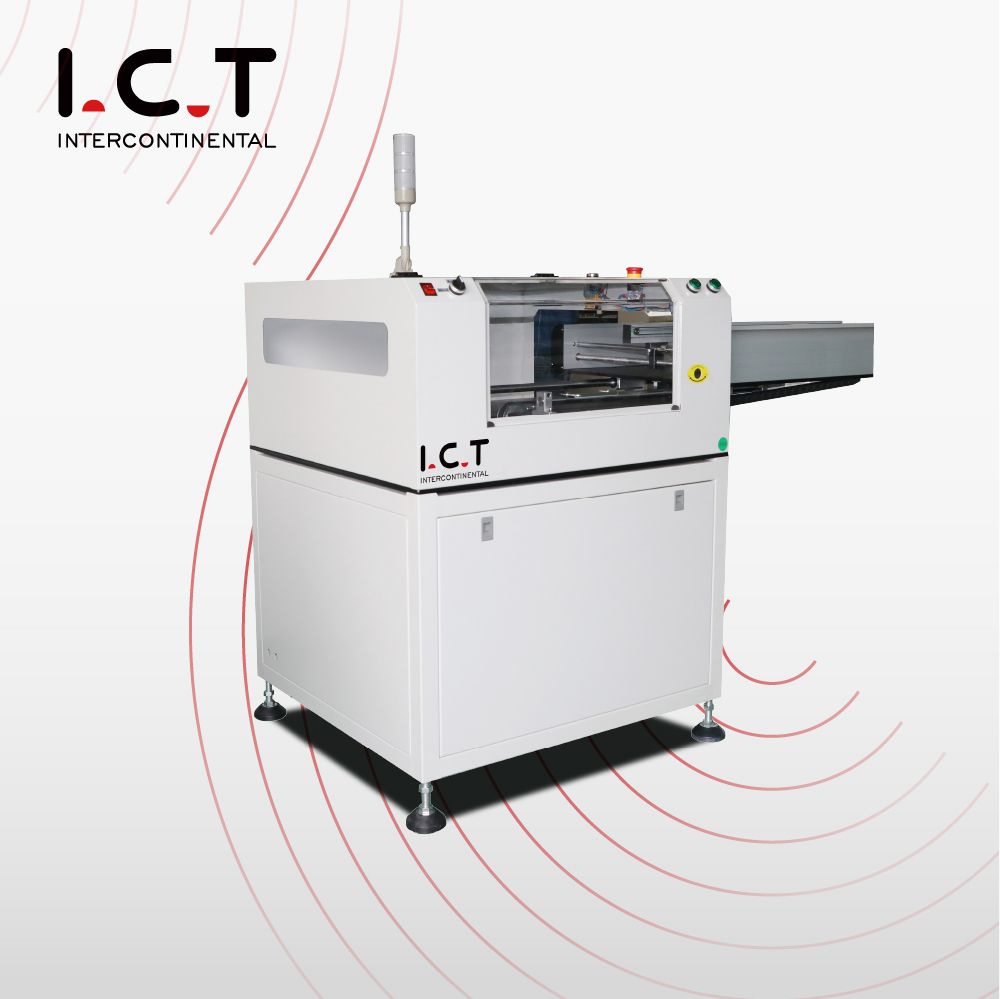

Working principle:
The track length can be adjusted to suit different PCB sizes or production requirements.
Features:
The transmission distance can be adjusted dynamically to improve the flexibility of the production line.
Get a Quote >>
2-5. SMT PCB Flipper / Inverter
Application:
PCB production that requires double-sided mounting
After SMT mounting is completed, turn it over for plug-in soldering

Working principle:
The PCB is rotated 180° through a pneumatic or mechanical flipping mechanism, suitable for double-sided processing.
Features:
Precise flipping, stable operation, suitable for double-sided patch and plug-in processes.
Get a Quote >>
2-6. SMT PCB Turn Conveyor / Diverter
Application:
Limited production line space, need to adjust PCB transmission direction
Connect equipment in different directions
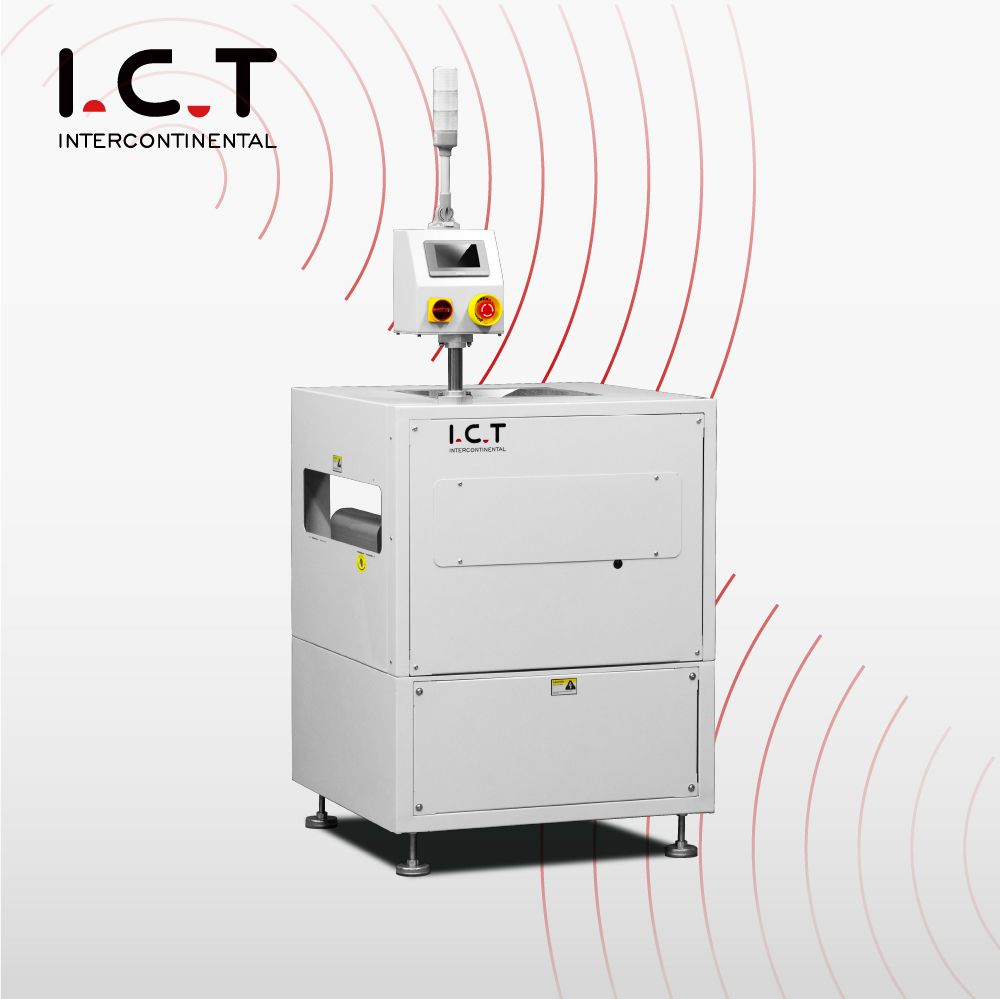

Working principle:
Used to redirect PCBs flow into different channels in a
production line(rotate 90°,180 °, 270 °).
Features:
Optimize production line layout, reduce floor space, and adapt to complex process requirements.
Get a Quote >>
2-7. SMT PCB Translation Shuttle Conveyor
Application:
High-speed production line, reducing the bottleneck of single-lane transmission;
Connection before and after dual-lane placement machine or dual-lane reflow soldering.
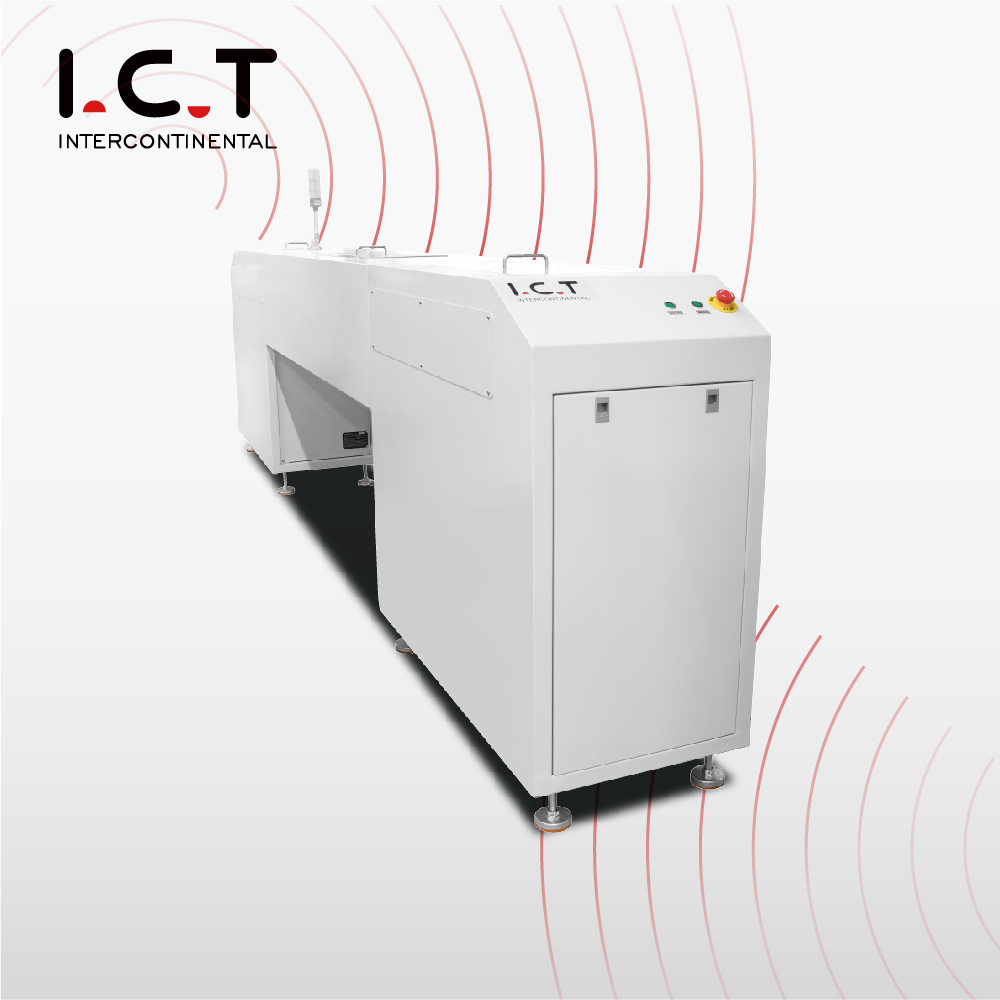

Working principle:
Through the horizontal moving mechanism, the PCB is moved from one track to another to achieve dual-track or multi-track transmission.
Features:
Support multi-track switching, improve production efficiency, suitable for dual-track or multi-track equipment.
Get a Quote >>
← Click the image for Video
2-8. SMT PCB Change Edge Machine ( PCB Rotating Conveyor )
Application:
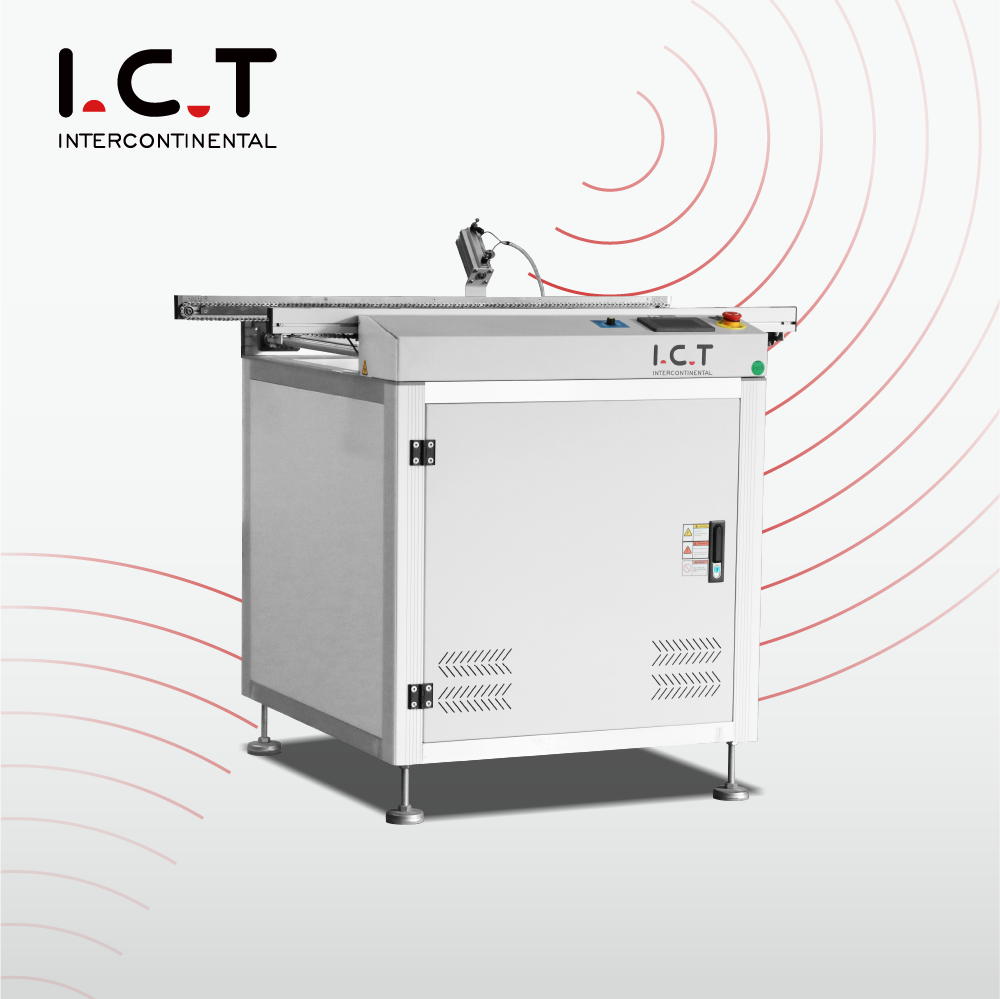

Working principle:
Through the rotating mechanism, the PCB is changed side by side (90° or 180°) to adjust the transmission direction or angle.
Features:
Suitable for production processes that require side changes and optimize equipment connection.
Get a Quote >>
← Click the image for Video
3. Automated Conveyor (Inline SMT Conveyor)
An automated conveyor integrates with equipment like robots and AOI on the SMT production line, enabling fully automated production, improving efficiency and product quality by automatically handling PCBs.
Working principle:
The automated conveyor connects with robots and AOI equipment to automatically transport and process PCBs. Robots place components, AOI inspects soldering quality, and the conveyor ensures smooth PCB transfer between devices during production.
Main features:
Efficient Transmission: Provides high-speed, stable PCB transport, reducing manual intervention and boosting efficiency.
Precise Conveyor: Works seamlessly with robots and AOI to ensure accurate PCB transfer and positioning.
Intelligent Control: Features an intelligent system that adjusts speed and path for flexible production.
Real-time Monitoring: Monitors production status in real time, quickly identifying and addressing issues.
Application:
Fully Automated SMT Line: Works with robots and AOI for unattended production.
High-Precision PCB Assembly: Ensures accurate PCB transfer for precise assembly.
Flexible Production: Enables quick switching for multi-variety, small-batch production.
Classification SMT Line conveyor Based on Application
In the electronics manufacturing industry, PCB conveyors can be used in a variety of production lines to meet specific process and production requirements depending on their application scenarios.
The following are some of the main application scenarios and their characteristics:
1. SMT production line:
Application: Connects equipment like printers, placement machines, and reflow soldering to ensure smooth PCB transmission.
Requirements: Precise positioning, adjustable speed, and high compatibility for high-speed, high-precision production.
2. Wave soldering production line:
Application: Guides PCBs to the wave soldering oven, ensuring soldering quality and consistency.
Requirements: High temperature resistance, prevents PCB warping, and maintains stable speed for effective soldering.
3. Plug-in component assembly production line:
4. Inspection and testing production line:
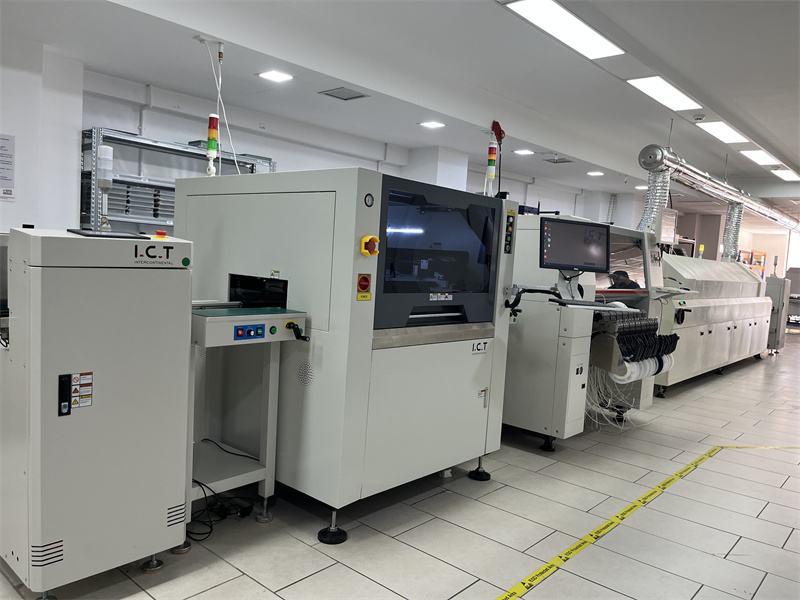

SMT Production Line
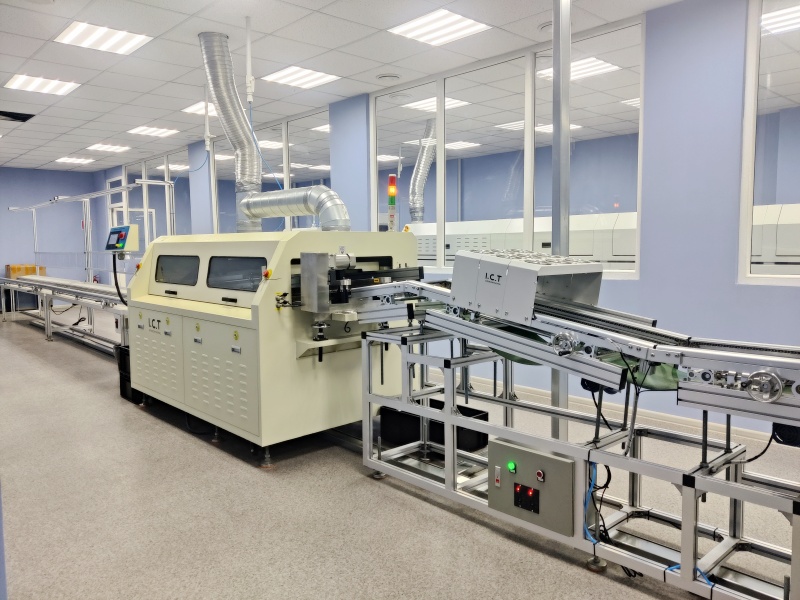

DIP Assembly Line
Want to enhance your production line? >>>
Classification PCB Conveyor Based on Material
In the SMT industry, SMT conveyors depending on the material, conveyors are mainly divided into two categories:
1. Metal Conveyors:
2. Plastic Conveyors:
When selecting the material for conveyors, it is important to consider the specific needs of the SMT production line, including environmental conditions, load requirements, and budget constraints, to ensure the equipment’s performance and reliability.
Classification PCB Handling Conveyor Based on Configuration
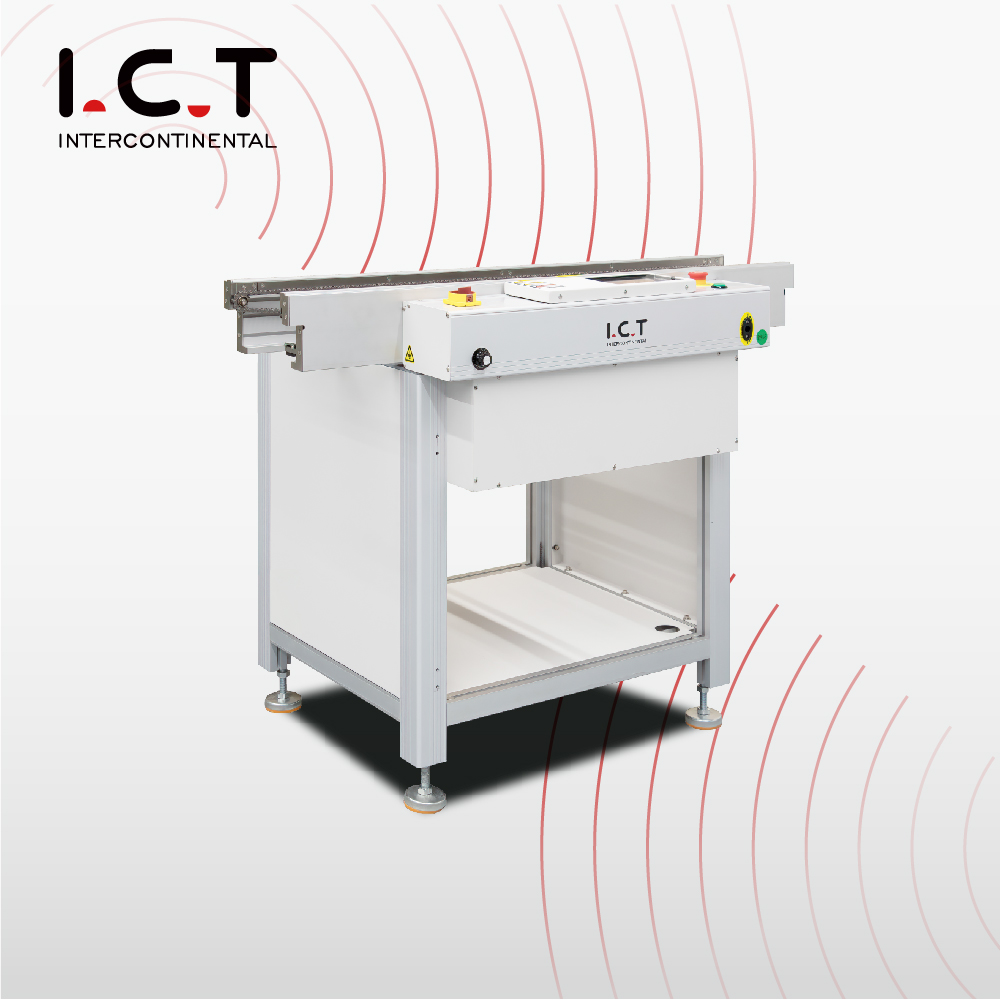

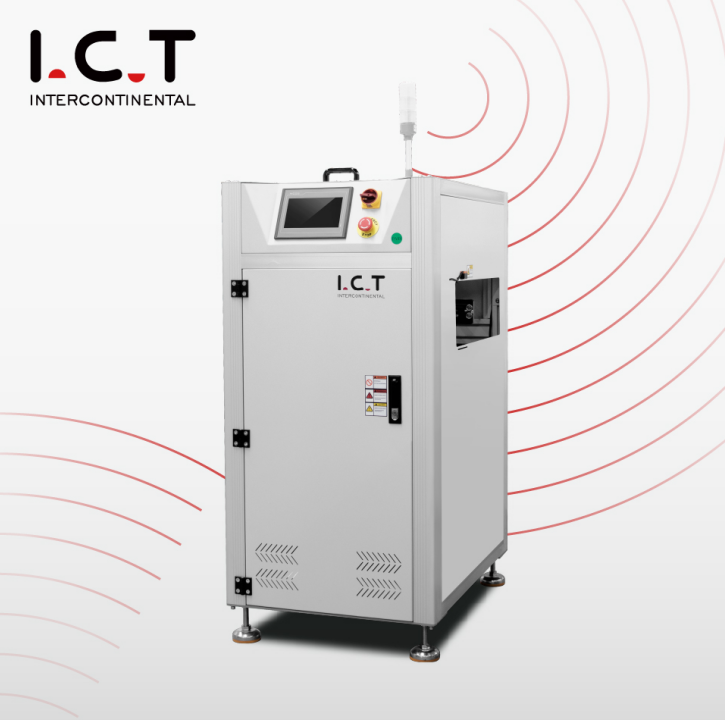
I.C.T High-end PLC PCB Conveyor
PLC-Based Conveyor
Advanced conveyors with programmable logic control (PLC).
Features a touch screen for real-time monitoring and custom programming.
Classification SMT Conveyor Belt Based on Speed
1. Low-Speed PCB Conveyor
2. High-Speed PCB Conveyor
How to choose the right SMT conveyor for your production?
Selecting the right PCB conveyor system depends on specific production needs, such as PCB size, processing speed, and automation level. Whether you need a chain conveyor for heavy-duty PCBs, a belt conveyor for precision handling, or an air floating conveyor for sensitive circuits, choosing the right equipment is essential for efficiency and quality.
For those looking to integrate high-performance SMT conveyors into their production lines, understanding these classifications can help make an informed decision. Are you looking for a reliable SMT conveyor manufacturer?
Contact us today to find the best solution for your PCB assembly conveyor needs! >>>
 English
English